Congress
5
- 7
Jun
SFMES / SFTS
Paris, France
Come and discover our products at the 17th SFMES-SFTS congress....
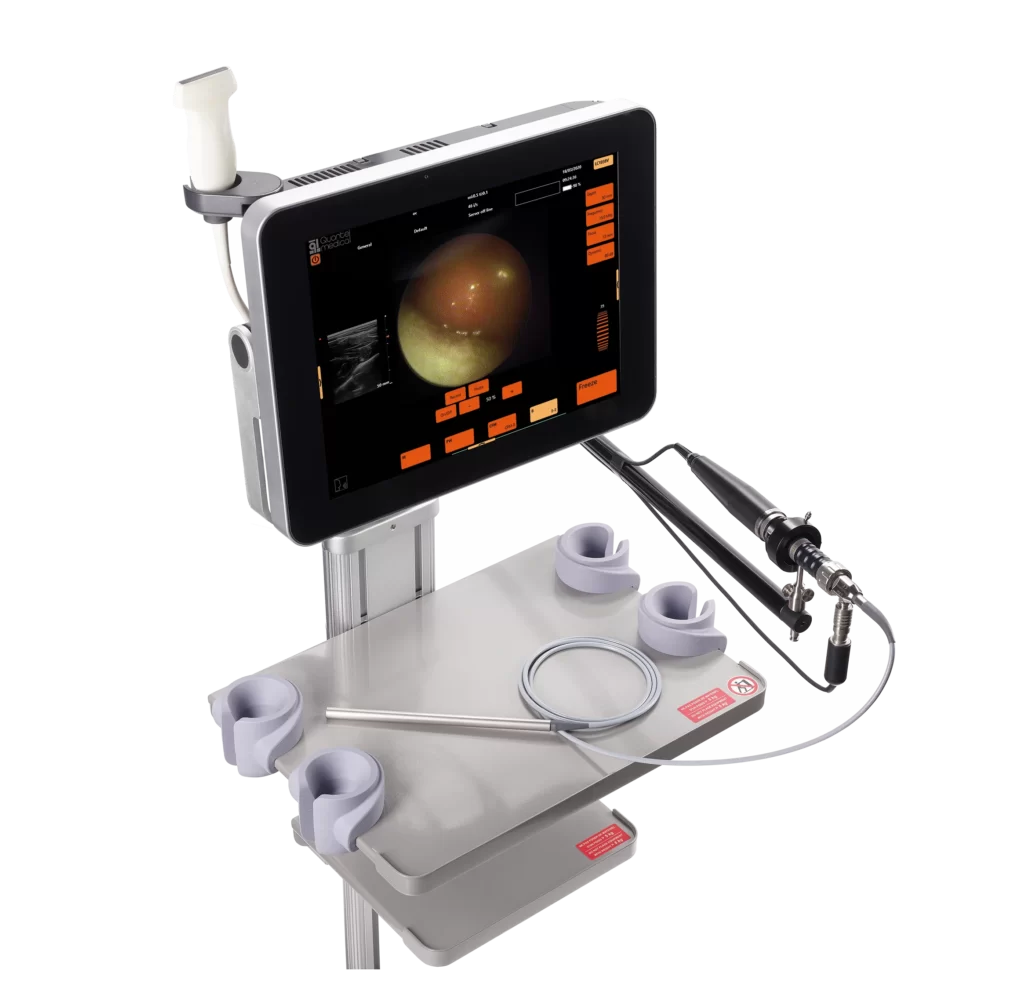
Coupling an ultrasound platform and a micro-endoscope in a single device, the 7StarScope brings new possibilities to interventional imaging.
It allows you to switch from procedures previously performed blind to procedures performed with direct vision, allowing you to “put your eyes directly at the tip of your needle”.
Lumibird Medical is the medical division of the Lumibird Group, an expert in fiber lasers, solid lasers, laser diodes, and medical equipment. Formed from the 2020 merger of three entities – Quantel Medical, Ellex and Optotek – specializing in diagnostic and treatment devices for ophthalmology, our company is recognized for its commitment to innovation and stands out as a world leader in ophthalmic equipment.
Since 2018, Lumibird Medical has extended its expertise to other medical specialties by offering a range of interventional imaging products that meet the needs of general practitioners, emergency, sport medicine, anesthesia/intensive care and much more… Interventional imaging uses imaging to perform a precise and less invasive diagnostic and therapeutic procedure than surgery. This technique results in less pain for the patient, less risk of infection, and shorter hospitalization and convalescence periods.
Because patient care is at the heart of our concerns, it is important to collect the experience of doctors who use our products.
Lumibird Medical offers a unique training programme for the introduction to clinical ultrasound that meets the expectations of healthcare professionals. This training, adapted to beginners, offers two learning modules, one for general medicine, the other for musculoskeletal medicine.